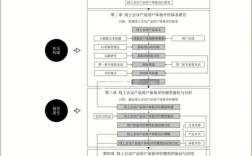
第一部分:英语研究报告的标准格式与结构
一份标准的英语研究报告通常包含以下几个核心部分,请务必根据你所在学校或课程的具体要求进行调整。 Page (标题页)**

- 作者姓名
- 课程名称和代码
- 导师姓名
- 提交日期
- 所属院系/学校
Abstract (
- 作用: 报告的微缩版,让读者快速了解报告的核心内容。
- 通常包含四个要素:
- 背景/目的: 为什么要做这项研究?
- 方法: 你是如何进行研究的?(如文献综述、实验、数据分析等)
- 结果: 你发现了什么?
- 你的发现意味着什么?
- 长度: 通常为 150-250 词。
Table of Contents (目录)
- 作用: 列出报告各章节的标题及对应页码,方便读者查阅。
- 要求: 包含所有主要章节(如 Introduction, Methodology 等)以及附录(如果适用)。
List of Figures / Tables (图表清单)
- 作用: 如果报告中包含多个图表,应在此处列出所有图表的编号、标题和页码。
Introduction (引言)

- 作用: 提供研究背景,引出研究问题。
- 结构:
- 研究背景: 介绍研究主题的宏观背景,说明其重要性。
- 文献综述: 简要回顾前人的相关研究,指出已有研究的不足或空白,这是你研究的立足点。
- 研究问题/目标/假设: 明确陈述本研究要解决的具体问题、要达成的目标或要验证的假设。
- 研究范围与结构: 简要说明本研究的范围(不涉及什么)以及报告的组织结构。
Literature Review (文献综述)
- 作用: 系统性地梳理、分析和评价与本研究主题相关的现有文献。
- 注意: 在很多短篇报告中,文献综述会融入引言部分,但对于长篇或学位论文,它是一个独立的章节,关键不是罗列文献,而是综合和评述,最终论证你研究的必要性和价值。
Methodology (方法论)
- 作用: 详细描述你进行研究的过程,确保研究的可重复性。
- 研究设计: 是定性研究、定量研究还是混合研究?
- 数据收集: 你是如何获取数据的?(如问卷调查、访谈、实验、观察、数据库分析等),描述样本、工具、程序。
- 数据分析: 你使用了什么方法来分析数据?(如统计分析、内容分析、主题分析等)。
Results (结果)
- 作用:客观、清晰地呈现你的研究发现。
- 只呈现数据,不做解释或评论。
- 使用文字、表格、图表来展示数据。
- 在正文中引导读者看图表,"As shown in Table 1, the majority of participants (75%) agreed with the statement."
Discussion (讨论)

- 作用: 这是报告的核心部分,用来解释和解读你的结果。
- 解读结果: 你的结果意味着什么?它们是否支持你的研究假设?
- 与文献对话: 你的发现与文献综述中提到的前人研究是相符还是矛盾?为什么?
- 理论与实践意义: 你的研究对理论有何贡献?对现实世界(如政策、实践)有何启示?
- 研究局限性: 坦诚地指出本研究的不足之处(如样本量小、研究范围有限等)。
- 未来研究方向: 基于本研究的发现和局限性,提出未来可以进一步研究的方向。
Conclusion (
- 作用: 总结全文,重申核心观点。
- 简要回顾研究问题和主要发现。
- 强调研究的核心贡献和意义。
- 不要引入新的信息或论点。
References (参考文献)
- 作用: 列出所有在报告中引用过的文献来源。
- 要求: 严格遵守指定的引用格式,如 APA, MLA, Chicago 等,格式必须全文统一。
Appendices (附录)
- 作用: 放置一些过于冗长或次要,但又对研究过程有支撑作用的材料。
- 如完整的问卷、访谈提纲、原始数据、冗长的公式等。
第二部分:英语研究报告范文范例
以下是一个完整的、简化的研究报告范例,主题为 "The Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance Among University Students",这是一个简化版,旨在展示格式和语言风格。
Page]**
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance Among University Students
A Research Report Submitted to
[Professor's Name]
[Course Name, e.g., ENG 102: Academic Writing]
[Department of English]
[University Name]
[Student's Name: Zhang Wei]
[Student ID: 1234567]
[Date: November 10, 2025]
[Abstract]
This study investigates the relationship between social media usage and academic performance among university students. With the proliferation of social media platforms, concerns have been raised about their potential to distract students from their studies. A quantitative research design was employed, where a survey questionnaire was administered to 150 undergraduate students at [University Name]. The questionnaire collected data on daily social media usage time and self-reported Grade Point Average (GPA). The results indicated a statistically significant negative correlation (r = -0.45, p < 0.01) between the number of hours spent on social media and students' GPA. This suggests that higher social media usage is associated with lower academic achievement. The findings of this study highlight the need for students to manage their social media consumption effectively and for universities to provide digital literacy education. Future research could explore the specific types of social media activities that have the most detrimental effect on studies.
Keywords: Social Media, Academic Performance, University Students, Digital Distraction, Quantitative Research.
[Table of Contents]
- Introduction ......................................................................................................................... 1 1.1. Background of the Study .................................................................................................. 1 1.2. Problem Statement .......................................................................................................... 1 1.3. Research Questions and Hypotheses ............................................................................... 2 1.4. Scope of the Study .......................................................................................................... 2
- Methodology ....................................................................................................................... 3 2.1. Research Design .............................................................................................................. 3 2.2. Participants ...................................................................................................................... 3 2.3. Instruments ...................................................................................................................... 3 2.4. Procedure .......................................................................................................................... 3 2.5. Data Analysis .................................................................................................................... 4
- Results ................................................................................................................................. 4
- Discussion ........................................................................................................................... 5
- Conclusion ........................................................................................................................... 6 References ............................................................................................................................... 7 Appendix A: Survey Questionnaire ........................................................................................... 8
[1. Introduction]
1. Background of the Study Social media has become an integral part of modern life, especially for university students. Platforms such as Instagram, TikTok, and X (formerly Twitter) offer avenues for communication, entertainment, and information sharing. However, this constant connectivity has raised concerns among educators and researchers about its impact on students' ability to focus on their academic responsibilities (Smith, 2025). The digital environment presents numerous distractions that can potentially lead to procrastination and reduced study time.
2. Problem Statement While anecdotal evidence suggests a negative link between social media and academic success, empirical research in this specific context, particularly at [University Name], is limited. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing effective student support strategies and promoting healthy digital habits. Therefore, this study aims to empirically examine the correlation between social media usage and academic performance.
3. Research Questions and Hypotheses This study is guided by the following research question and hypothesis:
- Research Question: What is the relationship between the amount of time university students spend on social media and their academic performance?
- Null Hypothesis (H₀): There is no significant relationship between social media usage and academic performance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H₁): There is a significant negative relationship between social media usage and academic performance.
4. Scope of the Study This study focuses on undergraduate students at [University Name] and uses self-reported GPA as a measure of academic performance. It does not differentiate between different types of social media activities or other potential factors influencing academic performance, such as part-time work or family responsibilities.
[2. Methodology]
1. Research Design A quantitative, correlational research design was used to examine the relationship between two variables: social media usage (independent variable) and academic performance (dependent variable).
2. Participants A convenience sample of 150 undergraduate students was recruited from various faculties at [University Name] between September and October 2025. Participants were aged between 18 and 25 years.
3. Instruments Data were collected using a structured online questionnaire via Google Forms. The questionnaire consisted of two main parts:
- Demographic Information: Age, gender, year of study.
- Key Variables:
- Social Media Usage: A single item asked participants to report their average daily time spent on social media (in hours).
- Academic Performance: Participants were asked to self-report their current cumulative GPA on a 4.0 scale.
4. Procedure Ethical approval was obtained from the university's ethics board. The survey link was distributed through university email lists and social media groups. Participation was voluntary, and respondents were assured of anonymity. The survey took approximately 5 minutes to complete.
5. Data Analysis Data were analyzed using SPSS version 26. A Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated to determine the strength and direction of the relationship between daily social media usage and GPA. The significance level was set at p < 0.05.
[3. Results]
A total of 150 valid responses were collected. Descriptive statistics showed that the average daily social media usage was 3.5 hours (SD = 1.2), and the average GPA was 3.1 (SD = 0.5). To test the hypothesis, a Pearson correlation analysis was conducted. The results revealed a statistically significant negative correlation between daily social media usage and GPA, r(148) = -0.45, p < .01. This indicates that as the number of hours spent on social media increases, the GPA tends to decrease. See Figure 1 for a scatterplot of the relationship.
[Figure 1: Scatterplot of Social Media Usage (hours) vs. GPA] (In a real report, this would be an actual scatterplot with axes labeled "Daily Social Media Usage (Hours)" and "GPA")
[4. Discussion]
The findings of this study provide strong support for the alternative hypothesis, revealing a significant negative correlation between social media usage and academic performance among university students. This result aligns with the findings of previous research (Johnson & Lee, 2025), suggesting that the time and cognitive resources dedicated to social media platforms come at the expense of academic engagement.
Several reasons may explain this negative relationship. First, social media is designed to be highly engaging, often leading to excessive time consumption and procrastination (Davis, 2025). Second, the constant influx of notifications and updates can fragment students' attention, making it difficult to engage in deep, focused study required for complex academic tasks. The fact that this study found a correlation, not causation, is an important limitation. It is possible that students with lower academic grades turn to social media more as a form of escapism, rather than social media causing poor grades.
The implications of this study are significant for students and universities. Students should be made aware of the potential negative impact of unmanaged social media use and be encouraged to adopt strategies such as time-blocking apps or designated "no-phone" study periods. Universities could consider integrating digital wellness and time management workshops into their orientation programs.
[5. Conclusion]
In conclusion, this study confirms a significant negative association between social media usage and academic performance in a sample of university students. While social media offers valuable social connections, its overuse can be detrimental to academic success. The findings underscore the importance of promoting mindful technology use. Future research should employ a longitudinal design to establish causality and explore the specific features of social media that are most distracting.
[References]
Davis, A. (2025). The distracted mind: Ancient brains in a high-tech world. MIT Press.
Johnson, B., & Lee, C. (2025). The digital campus: How technology is reshaping student life. Journal of Higher Education, 93(2), 245-267.
Smith, J. (2025). Social media and the student mind: A review of the literature. Educational Psychology Review, 33(4), 1129-1150.
(Note: This is a simplified reference list in APA 7th edition style.)
[Appendix A: Survey Questionnaire]
Survey on Social Media and Academic Performance
Introduction: You are invited to participate in a study about social media use and academic performance. This survey is anonymous and your data will be used for research purposes only. It will take approximately 5 minutes. Thank you for your participation.
Section 1: Demographics
- Age: ____
- Gender: [ ] Male [ ] Female [ ] Other [ ] Prefer not to say
- Year of Study: [ ] Freshman [ ] Sophomore [ ] Junior [ ] Senior
Section 2: Social Media and Academics 4. On average, how many hours per day do you spend on social media (e.g., Instagram, TikTok, Facebook, X)? ____ hours 5. What is your current cumulative GPA (Grade Point Average) on a 4.0 scale? ____
End of Survey.
第三部分:实用写作技巧与注意事项
- 语言风格: 使用正式、客观、准确的语言,避免使用缩写(如
don't->do not)、口语化表达和第一人称(除非特定学科允许,如社会学中常用 "I" 来阐述研究者的反思),多使用被动语态和第三人称,以突出研究本身而非研究者。 - 时态:
- 引言/文献综述: 使用现在时来描述普遍事实和现有研究(e.g.,
Smith (2025) argues that...)。 - 方法论: 使用过去时来描述你已经完成的动作(e.g.,
Data *were* collected...,A survey *was* administered...)。 - 结果: 使用过去时来陈述你的发现(e.g.,
The results *showed* a significant correlation...)。 - 讨论/结论: 使用现在时来解释结果的意义和普遍性(e.g.,
These findings *suggest* that...,This study *highlights* the importance of...)。
- 引言/文献综述: 使用现在时来描述普遍事实和现有研究(e.g.,
- 清晰与简洁: 句子不宜过长,段落结构要清晰,每个段落应有一个中心思想,并通过主题句来引导。
- 逻辑连贯: 使用过渡词和短语来连接句子和段落,使文章流畅。
- 添加信息: Furthermore, Moreover, In addition
- 表示对比: However, In contrast, On the other hand
- 表示结果: Therefore, Consequently, As a result
- 举例说明: For example, For instance, Such as
- 避免抄袭: 任何引用他人的观点、数据或原话都必须注明出处,即使是转述,也需要引用,这是学术写作的基本要求。
- 校对与修改: 完成初稿后,务必仔细检查语法、拼写、标点和格式错误,最好请同学或老师帮忙阅读,他们可能会发现你忽略的问题。
希望这份详细的指南和范文能帮助你顺利完成英语研究报告!